|
These are not your father's
bombs; in fact, they're your great-grandfather's bombs. Note that per the title
"Bombs of the World War," there was no "I" or "1" appended to it. That is
because as we learned in grammar class in elementary school while being
instructed on creating outlines, one does not assign a number "1" or a letter
"a" or "A" if there will be no number "2" or letter "b" or B." Since what we now
refer to as World War I
was "the war to end
all wars," there was no expectation that there would someday be a World
War II. Hence, up until the end of 1941, people referred to the 28 July, 1914
through 11 November, 1918 conflict simply as "the World War" or "the Great War."
But I digress. Many of the bombs shown here were tossed out of the cockpit by
either the pilot or back seat bomber/gunner. BTW, when I saw that the
Whitehead Aircraft
Torpedo supposedly had an 8,000 yard (24,000 feet, or 4.5 miles) range
running on compressed air, I figured something was amiss, so I looked it up. The
actual range was 800 yards (2,400 feet, or 0.45 mile).
Bombs of the World War
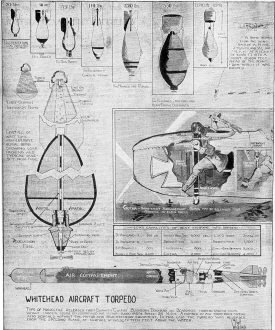 Bombing during the World War took some remarkable strides from the initial attempts
in 1914, when a few British ships carried the old jam-tin bombs, loaded with nails,
bolts, razor blades and old iron, which were hurled by hand from the cockpit. The
earliest attempt to carry bombs in racks saw a box arrangement set outside the cockpit,
with bottoms, out of which the early fragmentation bombs were released, Later the
first wing-racks were fitted, and this resulted in the release gear for the Whitehead
naval torpedo, used on the torpedo carriers developed in 1917. Actually, very few
bombs were dropped by hand, as flying in those days usually took all of the pilot's
attention, and few pilots cared to carry bombs loose in the cockpit. The evolution
of the aircraft bomb is one of the most interesting pages of war history. Bombing during the World War took some remarkable strides from the initial attempts
in 1914, when a few British ships carried the old jam-tin bombs, loaded with nails,
bolts, razor blades and old iron, which were hurled by hand from the cockpit. The
earliest attempt to carry bombs in racks saw a box arrangement set outside the cockpit,
with bottoms, out of which the early fragmentation bombs were released, Later the
first wing-racks were fitted, and this resulted in the release gear for the Whitehead
naval torpedo, used on the torpedo carriers developed in 1917. Actually, very few
bombs were dropped by hand, as flying in those days usually took all of the pilot's
attention, and few pilots cared to carry bombs loose in the cockpit. The evolution
of the aircraft bomb is one of the most interesting pages of war history.
Posted October 15, 2022
|



