|
These, what appear to
be official Boeing-Stearman drawings for the "Kaydet" biplane primary trainer, were
published in the October 1961 issue of American Modeler magazine. The set
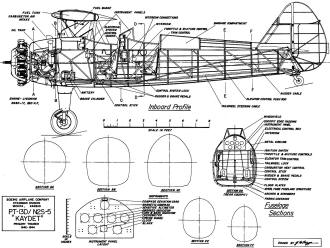
of three sheets provide a high level of detail on materials and construction. The
front view plan includes detail about the physical parameters as well as on instrumentation
and power. Of course this is far from a full set of construction plans, but if you
are building a scale model of the Boeing-Stearman Kaydet, the information should
be useful. Included in the article is a brief history of the relationship between
Boeing and Stearman, as well as on the formation of United Air Lines in 1928. According
to the author, the "Kaydet" was the last standard biplane produced for the Army
and Navy, more were manufactured than any other biplane design, with 10,346 being
completed between 1936 and the end of World War II.
Boeing-Stearman "Kaydet" Primary Trainer
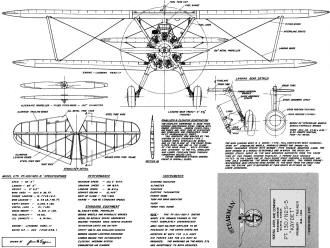
Boeing-Stearman "Kaydet" Primary Trainer plans, front view.
Incorporated by Lloyd Stearman in 1927, The Stearman Aircraft Company of Venice,
California and later of Wichita, Kansas was one of America's foremost pioneer aircraft
manufacturers. In 1927 and 1928 the Stearman Company was making a three-place commercial
open cockpit bipe and a convertible mail and passenger model around a basic design
with various powerplant installations. This three-place "Cloudboy" C3 commercial
model with its Wright J5 Whirlwind engine proved to be the most popular model and
the grand-daddy of famous "Kaydet" series.
By 1931 it was an established trend among major financial groups in America to
consolidate their various activities. An example was the formation of United Air
Lines as an operating company of the United Aircraft and Transport Corporation,
formerly the Boeing Airplane and Transport Corporation and incorporated in 1928.
United Air Lines consolidated the various airline subsidiaries of United Aircraft
and Transport: National Air Transport, Boeing Air Transport, Varney Air Lines and
Pacific Air Transport.
By 1933 United Aircraft and Transport held six manufacturing units along with
United Air Lines: Boeing Aircraft of Seattle, Washington; Sikorsky Aviation Corporation
of Bridgeport, Connecticut; Chance Vought, Pratt & Whitney and Hamilton Standard
Propeller of Hartford, Connecticut; as well as The Stearman Aircraft Company which
had been absorbed by United in 1929.
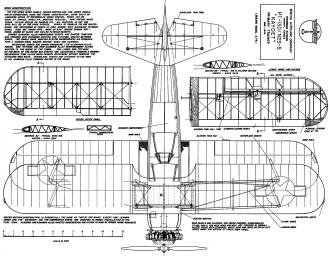
Boeing-Stearman "Kaydet" Primary Trainer plans, top view.
Boeing-Stearman "Kaydet" Primary Trainer plans, side view.
In the early 1930's, The Boeing Division at Seattle was developing and manufacturing
heavy commercial transports while the Stearman-Wichita plant was busy making commercial
biplanes. During this period Stearman also produced the Northrup Alpha and Beta
airplanes in the Wichita plant.
In 1936, Stearman Aircraft had become a subsidiary of the Boeing Airplane Company
and was designing and building training planes for the air forces, producing Model
75 for the Army and Model 73 for the Navy. Those were identical except for finish,
powerplants and minor installations. From the 73 and 75, Stearman developed Model
76 for domestic and export sale. Produced with several powerplants and a variety
of equipment, including floats and gun mountings, Model 76 was intended as an advanced
trainer, scout plane and light bomber. In 1936 Stearman also produced the 81, a
two-place biplane, basic trainer convertible to air-mail or military service. Powered
with a Pratt and Whitney Wasp Junior engine Model 81 was closer to the original
C3 biplane in appearance and design than the 73, 75 or 76.
Incorporating a variety of powerplants and minor equipment variations, all of
the "Kaydet" series airplanes produced were based on the basic 73 and 75 design.
In 1944 the PT-13D/N2S-5 model E75 was completely standardized for both the Army
and Navy with the same airplane carrying both services' designations and serial
numbers. Color scheme of this last of the "Kaydet" series was over-all silver with
the World War II "star and bar" type cockade markings on fuselage and wings.
The "Kaydet" was the last standard biplane produced for the Army and Navy, more
were manufactured than any other biplane design ... 10,346 being completed between
1936 and the end of World War II.
After the war, hundreds of surplus Boeing-Stearman "Kaydets" were purchased for
private use. Today the "Kaydet" remains in demand, particularly among crop-dusters.
With the front seat replaced by chemical spray tanks and a more powerful engine
installed-including the 450 hp Pratt & Whitney-the old "Kaydet" becomes an efficient
and practical duster-sprayer.
In addition to agricultural applications, modified "Kaydets" are in demand for
aerobatic work.
Additional Details Will Appear in Winter Edition of "Air Progress" - on sale
Nov. 28
Posted December 16, 2023
|